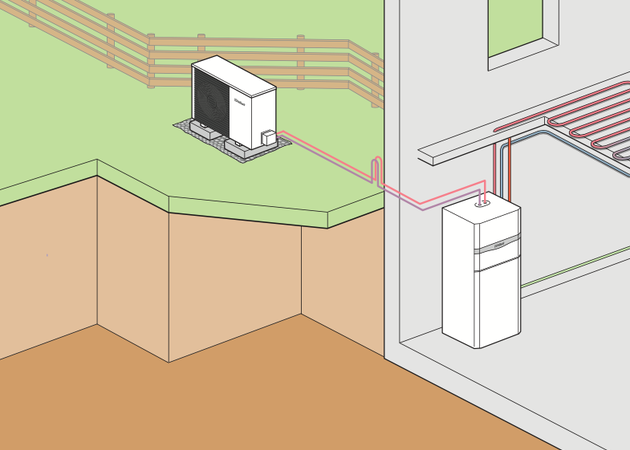
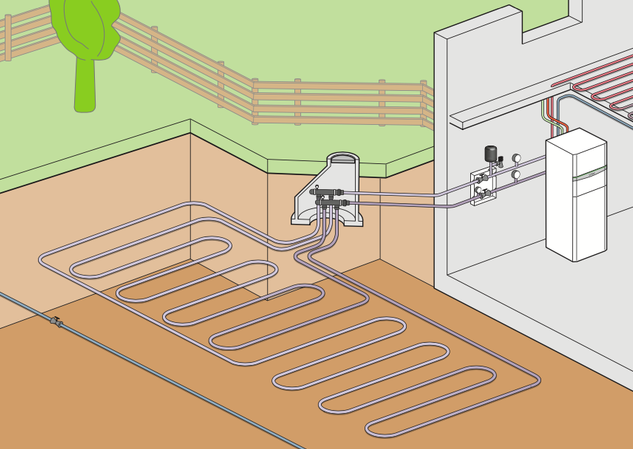
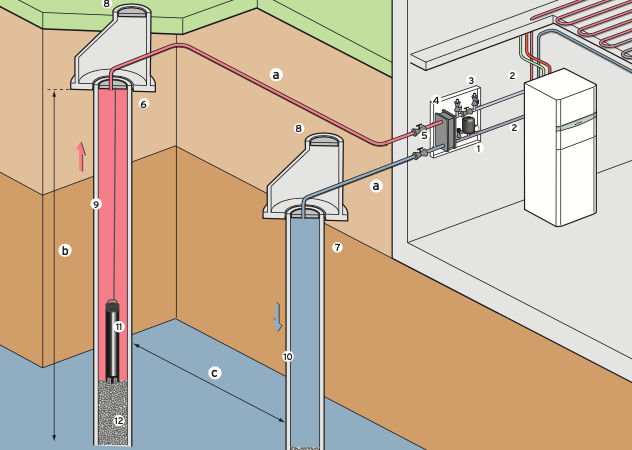
The heat pump is not only an efficient and sustainable heating system, but also an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil energy. Therefore - and this is yet another argument in favour of the heat pump - you can claim subsidies for switching to a heat pump. The heat pump uses energy from air, soil or groundwater and converts it into heating energy. In the following, we will answer the most important questions:
"How exactly does a heat pump work?". "What are the advantages of using a heat pump heating system?". "How much do the installation and operation cost?". "Is there anything else that needs to be taken into consideration?"
We have compiled all the information relating to heat pumps and have put it together for you in a way that is easy to understand.

Heat pump costs
If you are considering purchasing a heat pump, you will probably ask yourself this important question: what are the costs involved? The main costs are likely to be the acquisition and installation costs. Next come the operating costs, i.e. the cost of electricity to run the system. As for all heating systems, you also have to factor in an amount for maintenance costs.
In terms of acquisition and development, the air-source heat pump is usually the most affordable option - in this case you will have to invest approx. EUR 10,000 to 12,000. For ground-source heat pumps, you should expect to pay EUR 18,000 to 25,000 due to the necessary excavation work. For the purchase and installation of a water-source heat pump, you also have to spend about EUR 25,000, because you have to build an elaborate well system and that is correspondingly expensive.
Our tip: In new buildings, a geothermal heat pump is most likely "worthwhile", since it has to be built / dug. Suitable for this are our flexoTHERM exclusive and flexoCOMPACT exclusive.
The electricity costs depend on the age and size of the house, number of people living in the household, power rates, geographical location and much more. An important tip: Many utilities offer very favourable rates for the operation of heat pumps.
If you want an exact cost calculation for your heat pump, it is best to contact your installation company, who can go through the individual items with you step by step.
Planning of a new heat pump
First of all, and most importantly: Always seek advice from a qualified company once you have decided to install a heat pump. You should first check with a specialist about which type of heat pump solution is possible or advisable for you. Depending on which energy source you choose, you will have to be aware of unique characteristics.
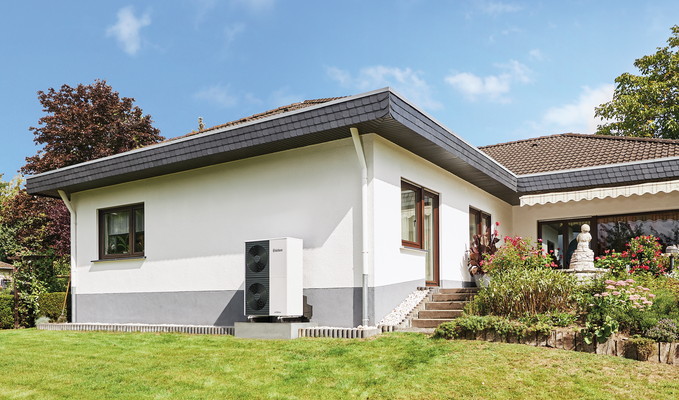

Modernising with a heat pump
You can plan the installation of a heat pump heating system in new buildings from the very start, but modernising your heating system with a heat pump is also highly recommended for old buildings. Vaillant offers solutions that enable heat pumps to work with underfloor heating as well as radiators. This is because underfloor heating is a panel heating system, which means that due to the larger radiator surface, you need a lower flow temperature when the system is in operation. As a result, the heat pump has to work less and is therefore more efficient.
Replacing oil heating systems is particularly worthwhile, because there is no longer any smell of oil, you gain an entire boiler room and you save money on operating costs.
Overall, modernisation involving a heat pump entails extensive work for you, especially if you have decided on a ground-source or a water-source heat pump. However, you shouldn't forget that you will have significantly lower operating costs from now on and are no longer dependent on fossil energy. In addition, by using a heat pump heating system, you are heating in an environmentally friendly manner and conserving natural resources.
Hybrid heat pump systems and system extensions
In multi-family houses, hybrid heating systems help to satisfy the high heating demand. In single-family homes, hybrid systems are usually used during renovation to expand existing and still functioning heating systems. If there is a high demand for hot water in a detached house, the system can be set up so that the gas provides hot water and the heat pump does the heating.
This is how a hybrid heat pump system works
A hybrid heat pump is a so-called bivalent system, which means that not just one, but two heat sources are utilised to provide heating. Usually the heat pump is combined with a gas heating system, but bivalent operation is also possible with an oil heating system. The heating system regulates which source is used automatically. When the difference between outside temperature and heating temperature is rather slight, the heat pump is able to heat efficiently. If the temperature difference increases, the gas or oil heating system takes over once a certain threshold is reached. Combining a heat pump with a gas or oil heating system makes a lot of sense, especially with an air-source heat pump.
A hybrid heating system consisting of oil or gas combined with a ground-source heat pump or a water-source heat pump is possible, but not practical. The reason is that the relatively constant temperature of the soil and groundwater means that there are no major fluctuations in electricity consumption.
Combination of heat pump and photovoltaic system
Heat pumps can be combined very effectively with a photovoltaic system. The photovoltaic system generates the electricity that the heat pump consumes when in operation. This has two advantages for you: On the one hand, you heat in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, and on the other hand, you make yourself a little less dependent on energy providers.
More possible heat pump combinations
Alternatively, you can use a bivalent system consisting of a heat pump and solar thermal energy. Unlike the photovoltaic system, this converts solar energy into heat instead of electricity.
Convenient operation is made possible by combining the heat pump with a control unit. From here, you can conveniently select the flow and setback temperature as well as many other settings in order to achieve the heating output that is right for you.
With a ventilation system, you not only ensure healthy air, but you also reduce your heating costs simultaneously. Your Vaillant technician will inform you in person about the possible combinations of your new heating system with a ventilation system.
Get in touch with us – we are happy to answer your questions!
Would you like to equip your home with a heat pump or do you have any questions?
Let us know your matter and give us your contact details. We will be happy to get in touch with you
Contact form